The Russian ZALA Lancet loitering munition has become one of the greatest dangers for the Ukrainian army, especially for the units operating in the near rear, such as anti-aircraft units and gunners.
Their use has become a significant threat, but what do we know about it?
In fact, the name “Lancet” combines a whole family of drones and their modifications produced by the Russian company Zala Aero. The drone we usually call “Lancet” is actually the older version of the drone with the name “Lancet-3.” Its smaller version, Lancet-1,” did not receive significant popularity.
However, even when discussing “Lancet-3” (hereafter ZALA Lancet,) we have to distinguish them because the loitering munition was repeatedly modernized and received changes in the design. In the war against Ukraine, the Russian invaders use two generations of Lancet drones, known under the Item 52 designation, and the next version of this drone — Item 51.
ZALA Lancet has an unusual aerodynamic wing arrangement. Two X-shaped wings are installed on the fuselage, providing flight and maneuverability. In the front part of the fuselage there is an optical sensor; in the center there is a warhead, a battery, and an electric motor; and in the tail part there is a thrust propeller. The drone’s airframe is made of composite material.
To use the drone, a crew deploys a drone control station that looks like a case, and a catapult for launch.

The operational range of drones is more than 40 kilometers. Some comparisons suggest that the maximum flight radius is about 50 km. Due to these characteristics, the drone is actively used by the invaders in counterbattery work and to destroy anti-aircraft systems.
According to the Oryx project, the cost of one UAV is about $35,000.
From 2019 to now, the ZALA Lancet has been modernized many times. After hostilities in Syria and later in Ukraine, the Russians replaced an optical sensor with a better one, and the type of wings and flap attachment, as well as communication facilities, were changed.

It is known from the wreckage of downed loitering munitions that they are equipped with a KZ-6, a three-kilogram shaped charge unassigned for such use, which is installed inside the fuselage thanks to the mounting foam.
KZ-6 is a shaped charge designed for demolition and engineering work. It contains up to 1.5 kg of TG-40 explosive and is able to penetrate, under ideal conditions, about 200 mm of armor.
Further development of Item 52, surprisingly enough, led to the creation of a drone known as Item 51. It featured a slightly modified fuselage design, with two identical X-wings in the front and the tail sections replaced by a single wing in the front and smaller flaps at the rear.

In addition, certain Russian sources claim that this version of the drone has been equipped with a new warhead of enhanced power, with the mass increased to 5 kg. However, it is difficult to ascertain the veracity of these claims at this time.
However, the issue of installing a new warhead in the drone has been long overdue due to the significant number of successful hits that have failed to cause critical damage to targets or any damage at all, even with a direct hit.
For the first time, drones were used by units of the Russian Special Operations Forces, such as the Senezh and Kubinka-2 detachments. But with the beginning of the Russian invasion, their use became widespread and covered a wider range of units. Thus, today among active users, in addition to the SOF, there are special forces of the GRU, the 76th and 98th Divisions of the Russian Airborne Forces, the Kascad unit of the 1st Army Corps of the Russian Armed Forces, as well as, in smaller numbers, some other units of the Russian Armed Forces, and mercenaries of PMC Wagner.
Due to the long range and the specifics of the tasks in the rear of the enemy, the drone is used together with the ZALA 421-16Е2 reconnaissance drone from the same manufacturer. The scout searches for the target in the preset sectors, after which the ZALA Lancet is launched at the detected target. On the descent phase of the flight, the loitering munition uses an optical sensor on board to finalize its reconnaissance of the target and dive onto it.
All this time, a reconnaissance drone is usually loitering at altitude above the target, which conducts live recording and confirms the defeat of the target or a miss on it. This is important, because, due to the disappearance of communication, the last meters to the target drone flies “blind” without operator control.
The problem of lack of communication is standard for all drones. It appears when the height of an unmanned aerial vehicle decreases, which is associated with such a phenomenon as a radio horizon and an increase in the number of radio signal interferences between the UAV and a control station, such as trees and buildings.
To solve this problem, relay drones are usually used to amplify and transmit a signal over a longer distance. There are also special software solutions that automatically perform the task without the operator’s participation.
It is worth noting that the reconnaissance UAVs accompanying the ZALA Lancet are not repeaters for it. All the time, the drone directly interacts with the control station.
One of the simplest and most effective countermeasures during the so-called trench war was the widespread use of operational mock-ups. The consumption of a limited number of drones for false targets means that the same loitering munitions will not be used against this equipment.
The photos below show a high-quality mock-up of the Soviet 2S1 Gvozdika self-propelled howitzer, which is a high-value target for ZALA Lancet.
A more difficult way to prevent the work of Russian UAVs is through the use of SIGINT and EW systems.
While the “Lancet” is in the air under the control of the operator during the reconnaissance of the target, it is vulnerable to EW means. However, after capturing the target, when the drone is already directed towards the target, jamming becomes useless because the drone goes offline.
There are cases of successful counteraction to drones by Ukrainian “Bukovel” and “Nota” EW stations, but it is difficult to assert the efficiency of the use of portable anti-drone guns.
Russian drones can try to shoot down existing anti-aircraft weapons, such as MANPADS or by just densely firing towards the drone from small arms. Recently, the gunners started actively using shotguns to shoot down a drone on the approach to the target with the help of a “cloud” of buckshot.
The preparation for the use of Russian loitering munitions, as well as their launch, can be tracked for specific changes on the battlefield. According to Serhiy Flash, the current versions of the ZALA Lancet do not have navigation module protection from electronic warfare. Therefore, before launching, the Russians turn off their EW at GPS frequencies so as not to interfere with the Lancet.
“At 1575 MHz there was round-the-clock Russian jamming that suddenly disappeared. The drones did not see GPS but suddenly saw it. So we are waiting for the ZALA Lancet,” says Serhiy.
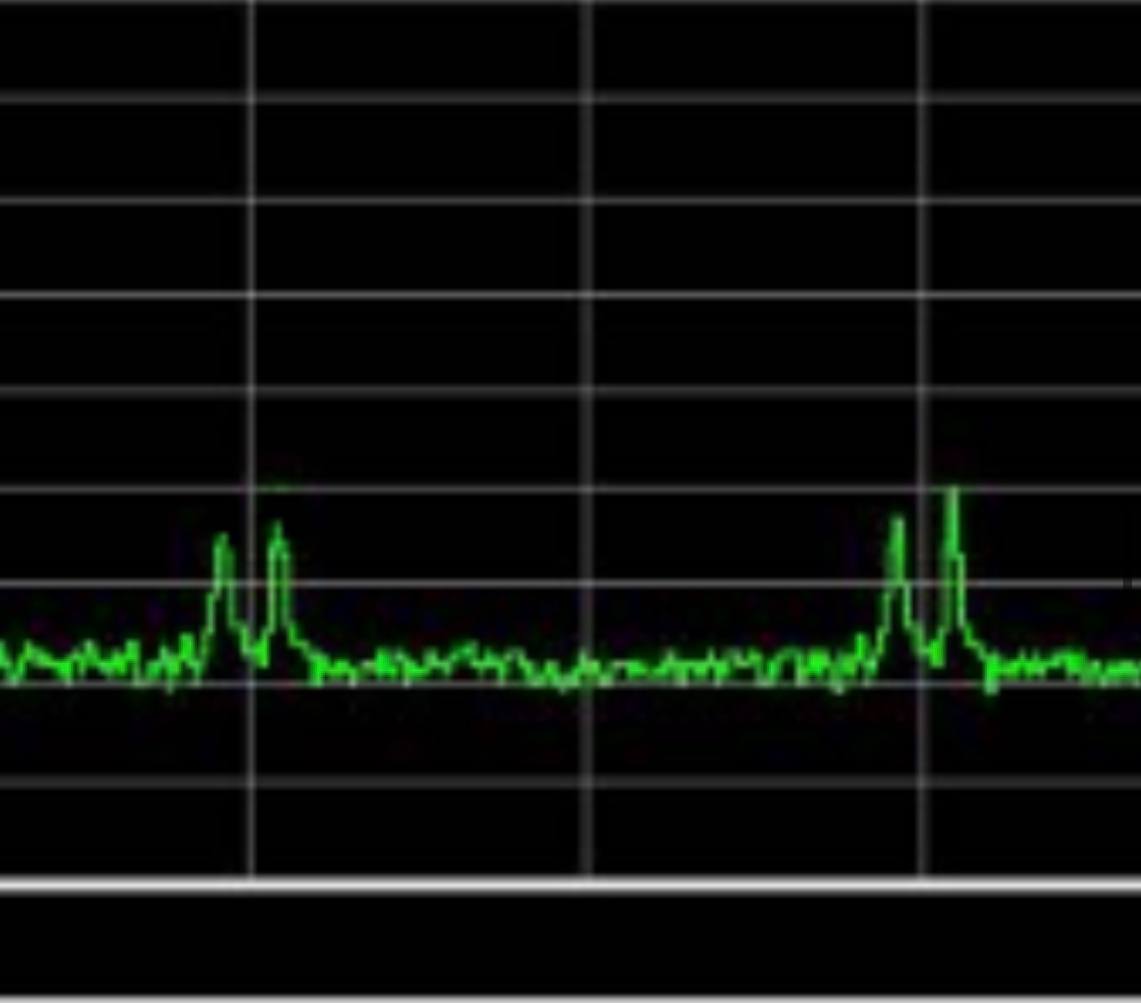
The operation of drones nearby can also be noticed due to radio frequency spectrum analyzers. So, drones from Zala, including the Lancet and their reconnaissance supporting UAVs work in the 900 MHz. More precisely, 868-870 MHz and 902-928 MHz. They have a specific shape, like two sharp peaks.
The latest “line of defense” against loitering munitions is the widespread use of anti-drone grids on positions, as well as the welding of metal grilles on equipment. These designs offer a good chance of survival by preventing drones from reaching the target.
In July 2023, Russian media announced the creation by Zala of a new generation of drones of the Lancet family under the Item 53 index.
The new generation of drones, according to propagandists, is expected to represent a significant leap forward, incorporating a network-centric swarm of drones. Each drone in the swarm will receive information about the target on the battlefield as soon as it is detected by any of the drones.
During the display of drone production, its pilot version was shown with folding wings, and with a launch system from transport-launch containers instead of the catapult-launch already traditional for these drones.

Such a launch scheme should facilitate their use as well as reduce their readiness time. Such a design will also allow the crew to launch several drones at once.

The Russians also announced the integration of new means of communication and guidance into UAVs, which are expected to neutralize any means of electronic warfare. Such statements, however, look like empty slogans without the use of any new revolutionary solutions that could replace standard means of communication.
The drone also began to use non-contact detonation of the warhead to bypass obstacles near the target, such as welded metal grilles and anti-drone grids.
Підтримати нас можна через:
Приват: 5169 3351 0164 7408 PayPal - [email protected] Стати нашим патроном за лінком ⬇
Subscribe to our newsletter
or on ours Telegram
Thank you!!
You are subscribed to our newsletter